The process starts with a three-day vulnerability assessment, where community members map their village, create a calendar of monthly activities, and discuss the biggest threats they see from climate change. Next, they work on an action plan to address those threats. Then, with support from their local government and IMACS, they work to implement the plan over time.
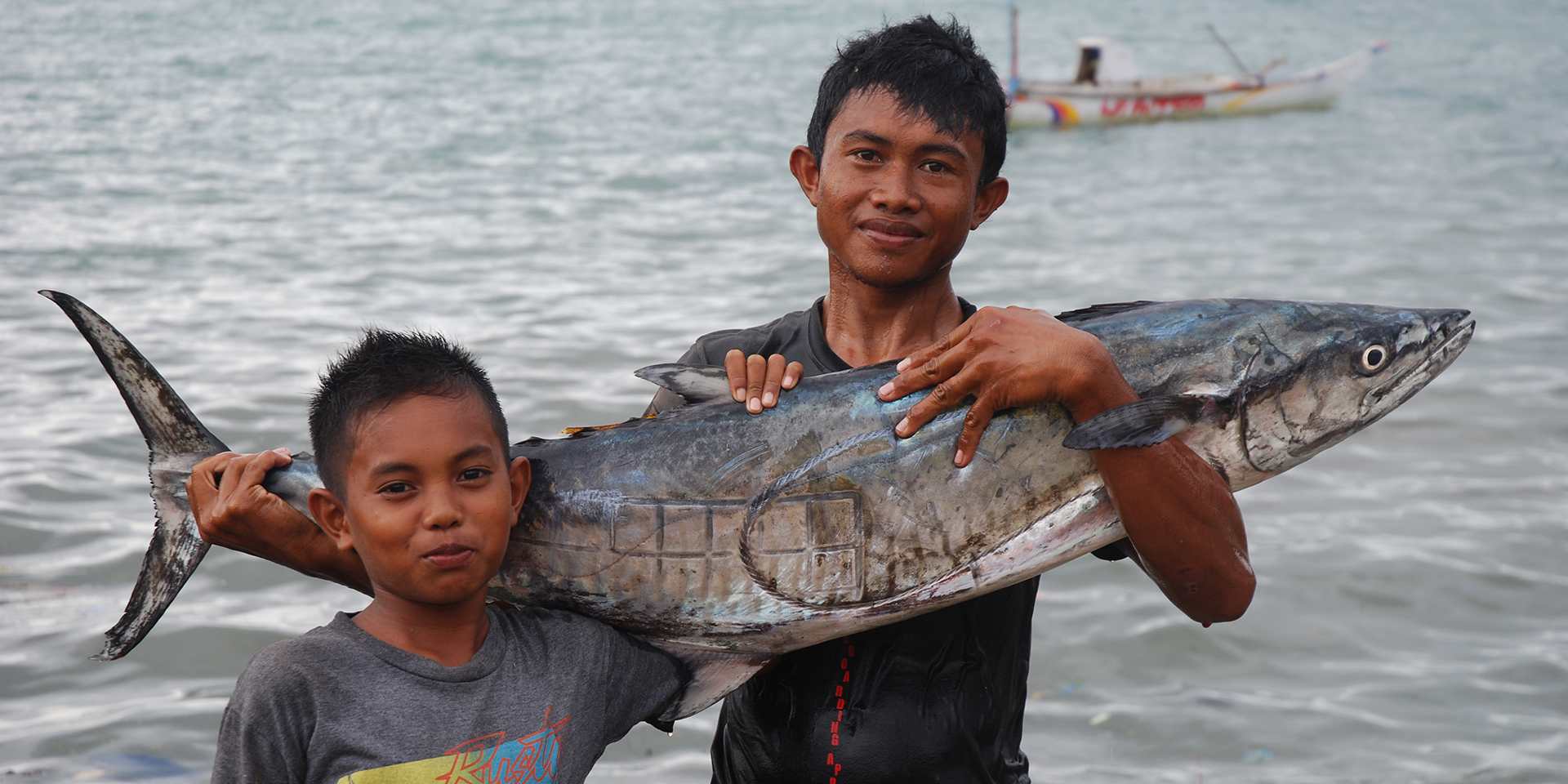
For example, the village of Liya Bahari decided their biggest problem was storms that prevent fisherman from working. So they developed seaweed farms as an alternative way for families to earn money. The government brought in seaweed industry experts, who worked with community members to implement the latest farming techniques and ensure success.
“The District Office of Marine Affairs and Fisheries supported the community in getting the right seaweed seeds,” La Ode Agus Rianto said.
In South Konawe, Rumba-rumba village built a 300-meter wall and planted new mangroves to protect their homes from rising seas, and expanded fish traps so fisherman don’t need to take their boats out under dangerous conditions. They also developed alternative industries to fishing that have allowed women to play a bigger role in the local economy. The women of the village now run a restaurant, a palm sugar business, and a fish-drying facility to preserve food for months when catches are more scarce.